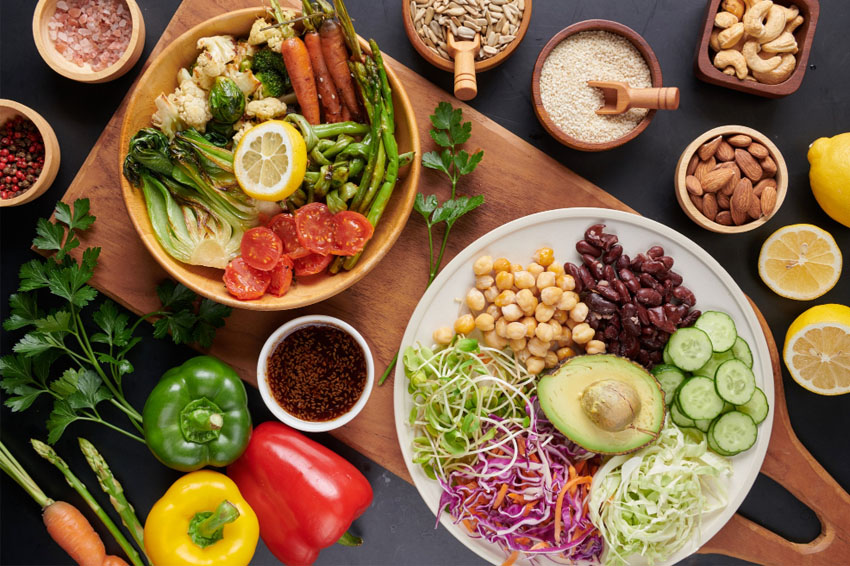
You must consume lots of fiber-rich foods, but you might also not understand why fiber is so necessary. Fiber benefits your health in a variety of aspects, including your gastrointestinal and digestive health.
Make sure you have lots of fiber-rich items on your plate. It will aid with digesting, minimize blood sugar rises, and make you feel complete and satisfied.
Why is Fiber Essential to Eat on a Frequent Basis?
To put things into perspective, dietary fiber is a plant-based carbohydrate that cannot be broken down into simple sugars. It can be found in entire plant meals.
Fiber intake reduces the speed of digestion assimilation and works as a gentle sweep for your intestines. This broom-like effect, together with uptake slowing, adds too many of its healing properties.
1. Promotes blood sugar stability
When fiber is ingested, it reduces the speed of digestion. As a result, the speed of sugar absorption in the circulation is slowed, providing a route for blood sugar regulation.
This is especially important since blood sugar rises and consequent decreases can occur when sugar is absorbed too rapidly.
Consuming whole meals high in fiber, such as vegetables, fruits, and whole grains, will help to reduce blood sugar increases.
2. Keeps you satisfied
Since fiber delays digestion, it also plays a large part in your body indicating that you’re satisfied and complete. When we ingest foods that are low in fiber, our bodies digest and absorb them fast. Over time, this might lead to a lack of fullness and completeness.
When fiber is available, food items are digested and absorbed significantly more slowly. This helps you to feel satisfied and energized for a longer amount of time.
We can slow down digestion and enhance fullness by including fiber in our diets on purpose.
Also read: Why Do People Take Nutritional Food Supplements?
3. Aids in the removal of waste from the body
Fiber, particularly insoluble fiber, functions like a small broom, cleaning your intestines and colon of build-up and can lower your risk of colon cancer.
Fiber also helps with gastrointestinal movement. It basically keeps things flowing in your bowels. This is what keeps your bowel motions regular and prevents constipation.
4. Maintains gut wellness
We know that our gut contains the bulk of our immune response, thus it’s essential that we start taking care of our gut health by feeding probiotics prebiotic-rich meals.
Fiber is a good source of prebiotics. Prebiotics also known as beneficial bacteria, in short, function as food for the probiotics that exist in our gut microbiome and help it grow.
A healthy digestive system and microbiota are enabled by a good balance of the two.
5. Keeps your heart healthy
Fiber can even contribute maintain good heart health. In a summary, digestion demands the release of bile acids, which are mostly composed of cholesterol.
The liver extracts cholesterol from the circulation to produce bile acids, which can lower LDL cholesterol levels in the body.
Understand that LDL is the bad cholesterol most closely related to an elevated risk of cardiovascular disease, so keep an eye on those LDL levels.
Also read: Is Salsa Healthy? Pros And Cons Of Salsa
How to Get Enough Fiber Optic Meals at Every Dish
To start, when you use the Foundational Five approach to construct proper meals, it directs you to include lots of fiber-rich foods on your plate at each mealtime.
This whole-food foundation is dense in nutrients, ensuring that all of your meals are well-balanced. However, it is essential to understand the many fiber food supplies as well as the various forms of fiber that might be included.
In that manner, you may be more thoughtful and purposeful about your decisions, reaping the health advantages mentioned above.
The many forms of fiber and their dietary sources: Soluble Fiber and Insoluble Fiber.
1. Soluble fiber
Soluble fiber dissolves in water. Bacteria ferment it as it goes through your digestive system, and it’s usually hydrophilic, which means it likes water. This kind of fiber absorbs water and gels in the digestive system. Soluble fiber, for example, has been shown to lower cholesterol, manage blood sugar levels, and boost digestive and immunological health.
Chia seeds contain a lot of soluble fiber. Soluble fiber-rich foods include – Beans, Avocado, Pears, Flax seeds, Apricots, Sweet potatoes, Chia seeds, and most Vegetables.
2. Insoluble fiber
Insoluble fiber does not dissolve in water. While a result, it does not change shape as it passes through your digestive system. This implies that it does not absorb water and gel-like soluble fiber.
Instead, nothing changes. Insoluble fiber improves regular bowel movements, accelerates waste evacuation via the colon, and keeps the intestines’ pH stable. Insoluble fiber-rich foods include – Lentils, Vegetables like Okra, Bran cereals, and most whole grains.
Do you include enough fiber in your food plate? Let us know in the comments section below.
Thumbnail Credit: Jcomp

Anvi has done Bachelor’s and Master’s in Nutrition and Dietetics. She’s planning to do a Ph.D. in Public Health Nutrition moving forward.